Life-Expectancy-Causal-Analysis
This project is maintained by emily-ramond
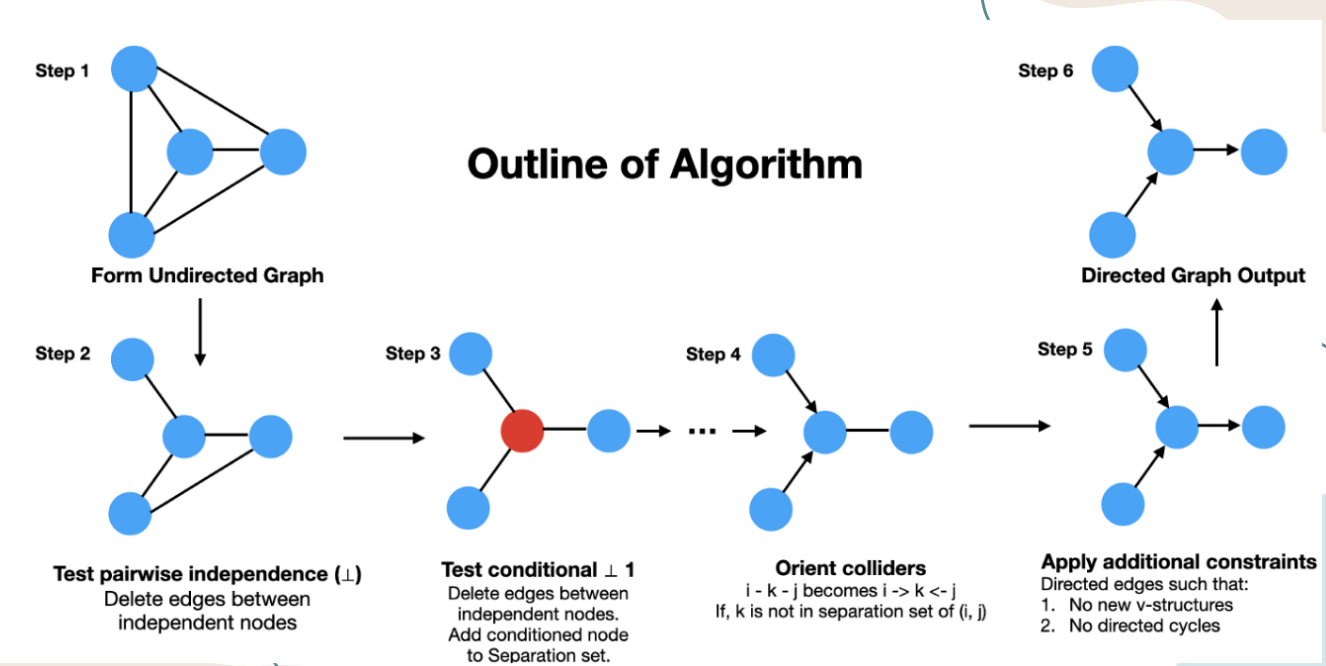
The PC Algorithm
We start with nodes all connected by undirected edges, ensuring there are no set distributions in place. We also use a significance level of .05. The lower the significance value, the smaller number of edges there will be in the graph. There are three steps the PC algorithm cycles through.
Step 1: In the first step, the PC algorithm identifies the skeleton by starting with a complete undirected graph. It removes the edge X-Y were X |_| Y | Z for some Z. In other words, edge X - Y is deleted if the corresponding variables X and Y are independent.
Step 2: After step 1, all left connected edges go through conditional independence testing. If there is no dependence, the variable is a separation set. This continues until there are no tests left to run.
Step 3: Now for any paths X-Z-Y in our working graph from the previous step, where There is no edge between X and Y as determined by Step 1 Z was not in the conditioning set that makes the variables X and Y conditionally independent. If these are true, then we know X-Z-Y forms an immortality Any edge Z-Y part of a partially directed path of the form X→ Z - Y where there is no edge connecting X and Y can be oriented as Z -> Y.
Once these steps have been cycled through and completed, and there are no more checks to run, the graph with directed edges is complete and we can start inferring information from that graph and associated variables, and in this case, causal dependencies have been oscillation patterns. It is important to note that a downside of conditional independence testing is that it is only efficient with infinite data.
Below is a visualization of this process:
Return back home by clicking here.